Filtering articles
Purpose
When the number of articles stored by FreshRSS inevitably grows larger, it’s important to use efficient filters to display only a subset of the articles. There are several methods that filter with different criteria. Usually those methods can be combined.
By category
This is the easiest method. You only need to click on the category title in the side panel. There are two special categories at the top of the panel:
- Main feed displays only articles from feeds marked as available in that category
- Favourites displays only articles marked as favourites
By feed
There are several methods to filter articles by feed:
- by clicking the feed title in the side panel
- by clicking the feed title in the article details
- by filtering in the feed options from the side panel
- by filtering in the feed configuration
By status
Each article has two attributes that can be combined. The first attribute indicates whether or not the article has been read. The second attribute indicates if the article was marked as favorite or not.
In version 0.7, attribute filters are available in the article display dropdown list. With this version, it’s not possible to combine filters. For instance, it’s not possible to display only read and favorite articles.
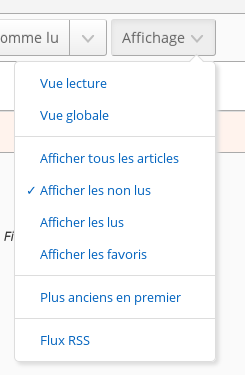
Starting with version 0.8, all attribute filters are visible as toggle icons. They can be combined. As any combination is possible, some have the same result. For instance, the result for all filters selected is the same as no filter selected.
By default, this filter displays only unread articles
By content
It is possible to filter articles by their content by inputting a string in the search field.
With the search field
You can use the search field to further refine results:
- by feed ID:
f:123or multiple feed IDs (or):f:123,234,345 - by category ID:
c:23or multiple category IDs (or):c:23,34,45 - by author:
author:nameorauthor:'composed name' - by title:
intitle:keywordorintitle:'composed keyword' - by text (content):
intext:keywordorintext:'composed keyword' - by URL:
inurl:keywordorinurl:'composed keyword' - by tag:
#tagor#tag+with+whitespaceor#'tag with whitespace' - by free-text:
keywordor'composed keyword' - by date of discovery, using the ISO 8601 time interval format:
date:<date-interval>- From a specific day, or month, or year:
date:2014-03-30date:2014-03ordate:201403date:2014
- From a specific time of a given day:
date:2014-05-30T13date:2014-05-30T13:30
- Between two given dates:
date:2014-02/2014-04date:2014-02--2014-04date:2014-02/04date:2014-02-03/05date:2014-02-03T22:00/22:15date:2014-02-03T22:00/15
- After a given date:
date:2014-03/
- Before a given date:
date:/2014-03
- For a specific duration after a given date:
date:2014-03/P1W
- For a specific duration before a given date:
date:P1W/2014-05-25T23:59:59
- For the past duration before now (the trailing slash is optional):
date:P1Y/ordate:P1Y(past year)date:P2M/(past two months)date:P3W/(past three weeks)date:P4D/(past four days)date:PT5H/(past five hours)date:PT30M/(past thirty minutes)date:PT90S/(past ninety seconds)date:P1DT1H/(past one day and one hour)
- From the oldest until some time before now:
!date:P1M(older than one month before now, using a negation)- Note: the syntax
date:/P1M
- Note: the syntax
- Date constraints may be combined:
date:P1Y !date:P1M(from one year before now until one month before now)
- From a specific day, or month, or year:
- by date of publication, using the same format:
pubdate:<date-interval> - by date of user modification, using the same format:
userdate:<date-interval> - by custom label ID
L:12or multiple label IDs:L:12,13,14or with any label:L:* - by custom label name
label:label,label:"my label"or any label name from a list (or):labels:"my label,my other label" - by several label names (and):
label:"my label" label:"my other label" - by entry (article) ID:
e:1639310674957894or multiple entry IDs (or):e:1639310674957894,1639310674957893 - by user query (saved search) name:
search:myQuery,search:"My query"or saved search ID:S:3or multiple search IDs:S:1,2- internally, those references are replaced by the corresponding user query in the search expression
Be careful not to enter a space between the operator and the search value.
Some operators can be used negatively, to exclude articles, with the same syntax as above, but prefixed by a ! or -:
!f:234, -author:name, -intitle:keyword, -inurl:keyword, -#tag, !keyword, !date:2019, !date:P1W, !pubdate:P3d/.
It is also possible to combine keywords to create a more precise filter.
For example, you can enter multiple instances of f:, author:, intitle:, intext:, inurl:, #, and free-text.
Combining several search criteria implies a logical and, but the keyword ` OR `
can be used to combine several search criteria with a logical or instead: author:Dupont OR author:Dupond
You don’t have to do anything special to combine multiple negative operators. Writing !intitle:'thing1' !intitle:'thing2' implies AND, see above. For more pointers on how AND and OR interact with negation, see this GitHub comment.
Additional reading: De Morgan’s laws.
ℹ️ Searches are applied to the HTML content, and special XML characters
<&">are automatically encoded (so one can search for'A & B'without having to encode the&). To search HTML tags, one must use regex searches (see below).
Finally, parentheses may be used to express more complex queries, with basic negation support:
(author:Alice OR intitle:hello) (author:Bob OR intitle:world)(author:Alice intitle:hello) OR (author:Bob intitle:world)!((author:Alice intitle:hello) OR (author:Bob intitle:world))(author:Alice intitle:hello) !(author:Bob intitle:world)!(S:1 OR S:2)
ℹ️ If you need to search for a parenthesis, it needs to be escaped like
\(or\)or used inside a quoted string like"a (b)"
Regex
Text searches (including author:, intitle:, inurl:, #) may use regular expressions, which must be enclosed in / /.
Regex searches are case-sensitive by default, but can be made case-insensitive with the i modifier like: /Alice/i
Supports multiline mode with m modifier, like: /^Alice/m
ℹ️
author:is working with one author per line, so the multiline mode may advantageously be used, like:author:/^Alice Dupont$/imℹ️
#is likewise working with one tag per line, so the multiline mode may advantageously be used, like:#/^Hello World$/im
Example to search entries, which title starts with the Lol word, with any number of o: intitle:/^Lo+l/i
Example to search empty entries (where the body of articles is blank): intext:/^\s*$/
As opposed to normal searches, special XML characters <&"> are not escaped in regex searches, to allow searching HTML code, like: /Hello <span>world<\/span>/
ℹ️ A literal slash needs to be escaped, like
\/
⚠️ Advanced regex syntax details depend on the regex engine used:
- FreshRSS filter actions such as auto-mark-as-read and auto-favourite use PHP preg_match.
- Regex searches depend on which database you are using:
- For SQLite, PHP preg_match is used;
- For PostgreSQL;
- For MariaDB;
- For MySQL.
ℹ️ Even with PostgreSQL, you are welcome to use
\bfor word boundary (and\Bfor the opposite), as there is an automatic translation to\yand\Y.
By sorting by date
You can change the sort order by clicking the toggle button available in the header.
Bookmark the current query
Once you came up with your perfect filter, it would be a shame if you had to recreate it every time you need to use it.
Luckily, there is a way to bookmark them for later use. We call them user queries. You can create as many as you want, the only limit is how they will be displayed on your screen.
Read more about user queries to learn how to create them, use them, and even reshare them via HTML / RSS / OPML.
Read more: